Parameter estimation for PEtab/SBML models using parPE¶
Introduction¶
This document describes how to set up and use parPE to estimate parameters for a model in the PEtab format. This is currently the most streamlined use case parPE.
PEtab is a convention to specify systems biology parameter estimation problems in a machine-readable way. It is based on SBML models and a set of tab-separated values files. Further information and a detailed format description are provided in the PEtab repository.
For testing, there is also an example shipped with parPE ../examples/parpeamici/steadystate/ and there is a collection of Benchmark Problems for Dynamic Modeling of Intracellular Processes with a variety of example problems.
Workflow overview¶
A rough overview of the workflow for setting up and using parPE to optimize a PEtab-based problem is provided in the following figure:
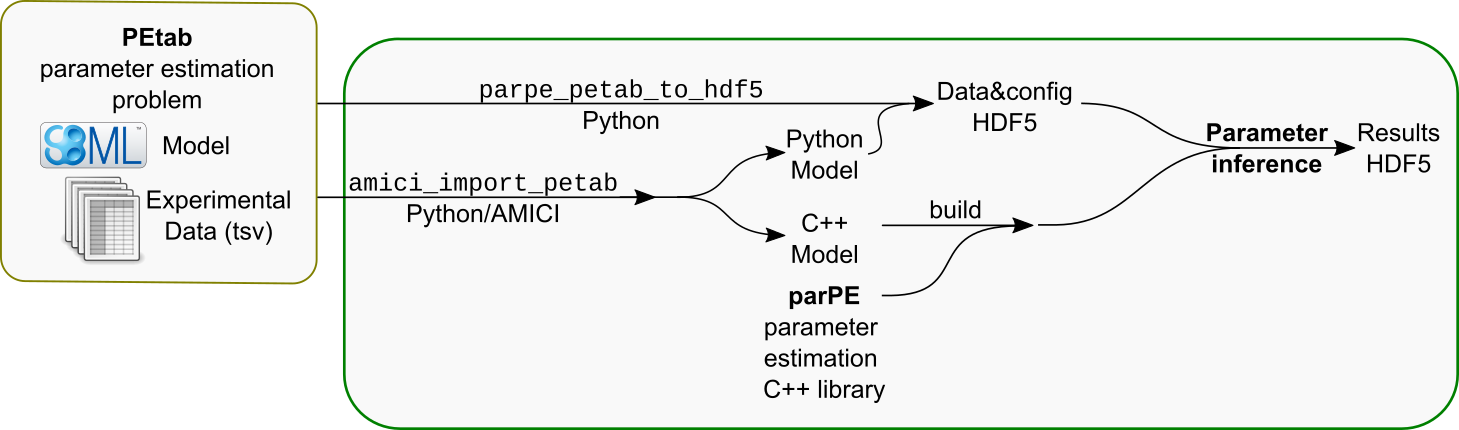
The principal steps are:
Building parPE as described in the documentation
Generating model C++ code and Python module (using
amici_import_petabfrom AMICI)Setting up a project for building parameter estimation (and other) executables for the given model (using ../misc/setup_amici_model.sh)
Generating an HDF5 input file for parPE with data and options for parameter estimation based on the PEtab problem definition (using
parpe_petab_to_hdf5from the parPE Python package.Running the desired optimization and further analysis
Any of these steps can be adapted to your specific needs. This document will present the simplest use case.
NOTE: This workflow is to be simplified and converted to a configurable Snakemake-based workflow. A scaffold is provided in ../snakemake/.
Notation¶
To not rely on a specific model, we will use generic artifact names throughout
this document. They will be written as some ${SOME_ARTIFACT}, so that
you just copy any commands after setting the respective shell variable to your
required values.
We will refer to the following artifacts:
${PETAB_YAML_FILE}: The PEtab YAML file (references all PEtab files belonging to the given parameter estimation problem)${AMICI_MODEL_DIR}: Output directory to be created where AMICI model code will be written to${MODEL_NAME}: Any name for the model${PARPE_SOURCE_ROOT}: Path to the parPE repository root directory${PARPE_MODEL_DIR}: Project directory for generating model-specific parameter estimation executables. Will be created, must not exist.${ESTIMATE}: Generated parameter estimation executable, see below${H5_PE_INPUT}: Generated HDF5 file for input to parameter estimation executable, see below
Building PEtab¶
Build parPE as described in the documentation.
Model processing¶
Although generally any kind of model can be used with parPE after, we will only describe the simplest case of using AMICI models. We assume that there is already a set of PEtab files with the problem definition. (This is not strictly necessary for using parPE, but will require significant additional effort).
We will use amici_import_petab for generating AMICI C++ model files and
Python package for the respective model. After installing AMICI, this
script should in your $PATH automatically.
NOTE: Use the AMICI version shipped with parPE (deps/AMICI). Do not try to
mix different versions of AMICI-generated models and AMICI base files. This
will likely lead to crashes and/or undefined behaviour.
Run:
amici_import_petab -v \
-o ${AMICI_MODEL_DIR} \
-n ${MODEL_NAME} \
-y ${PETAB_YAML_FILE}
Which will create ${AMICI_MODEL_DIR} containing model C++ files and a Python
package for the model.
Run amici_import_petab -h for further command line options.
Building parameter estimation executable¶
Next we need to create a new project to build the executables for parameter
estimation. The misc/setup_amici_model.sh script will do that, using the
C++ code generated by AMICI. It will adapt some templates for main.cpp files
and will build the targets using CMake:
${PARPE_SOURCE_ROOT}/misc/setup_amici_model.sh ${AMICI_MODEL_DIR} ${PARPE_MODEL_DIR}
After that, among other files, there should now exist an executable
${PARPE_MODEL_DIR}/build/estimate${MODEL_NAME} which will be used in the
second next step.
To simplify notation:
export ESTIMATE=${PARPE_MODEL_DIR}/build/estimate${MODEL_NAME}
Generating an HDF5 input file for parPE parameter optimization¶
The default workflow requires training data and optimization options to be
provided in an HDF5 file. Based on the PEtab problem definition, we can simply
create this using the parpe_petab_to_hdf5 script from the parPE Python
package:
parpe_petab_to_hdf5 \
-n ${MODEL_NAME} \
-y ${PETAB_YAML_FILE} \
-d ${AMICI_MODEL_DIR} \
-o ${H5_PE_INPUT}
This should create ${H5_PE_INPUT}. The file format is described in
hdf5.md This file will contain some default
settings. Those can be adapted using hdfview, your programming language of
choice, or from the command line using
../misc/optimizationOptions.py (-h for
usage information).
To inspect the default settings, run:
${PARPE_SOURCE_ROOT}/misc/optimizationOptions.py ${H5_PE_INPUT}
Running parameter optimization and further analyses¶
For running parameter estimation with default settings on a single node, run:
${ESTIMATE} -o test_output_dir/ ${H5_PE_INPUT}
Note that, depending on your model and data, this may take a long time.
The results will be written to HDF5 files in test_output_dir/. The output
format is described in hdf5.md.
Usage of the generated executable is described in more depth, for example, in the Jupyter notebooks in ../examples/parpeamici/steadystate/. These notebooks also demonstrate the use of other executables created earlier and show examples for data analysis using the parPE Python package.
